Android Java : List Selector Dialog class
This is a simple List Selector Dialog class to create simple pop-up lists in Android. It can handle 2 lists that
represent keys and values, both of which are sent back to the calling interface. This class does not handle
multiple item selection.
This class can handle Standard Java String[] arrays, ArrayLists, or HashMaps
The dialog class: Name this ListSelectorDialog.java. put it in the src/ directory of your project.
package com.yourpackage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.AlertDialog.Builder;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
public class ListSelectorDialog {
Context context;
Builder adb;
String title;
// our interface so we can return the selected key/item pair.
public interface listSelectorInterface {
void selectedItem(String key, String item);
void selectorCanceled();
}
ListSelectorDialog(Context c) {
this.context = c;
}
ListSelectorDialog(Context c, String newTitle) {
this.context = c;
this.title = newTitle;
}
ListSelectorDialog setTitle(String newTitle) {
this.title = newTitle;
return this;
}
ListSelectorDialog show(ArrayList il, final listSelectorInterface di) {
String l[] = null;
l = il.toArray(new String[il.size()]);
show(l, l, di);
return this;
}
ListSelectorDialog show(ArrayList il, ArrayList ik,
final listSelectorInterface di) {
// convert the ArrayList's to standard Java arrays.
String l[] = null; String k[] = null;
l = il.toArray(new String[il.size()]);
k = ik.toArray(new String[ik.size()]);
show(l, k, di);
return this;
}
ListSelectorDialog show(HashMap hashmap, final listSelectorInterface di) {
// convert the hashmap to lists
String[] il = new String[hashmap.size()];
String[] ik = new String[hashmap.size()];
// HashMap iteration
int i = 0;
for (Object key: hashmap.keySet()) {
il[i] = key.toString();
ik[i] = hashmap.get(key).toString();
i++;
}
// now show the selection dialog
show(il, ik, di);
return this;
}
ListSelectorDialog show(final String[] itemList, final listSelectorInterface di) {
// if only 1 list supplied, the list serves as both keys and values.
show(itemList, itemList, di);
return this;
}
ListSelectorDialog show(final String[] itemList, final String[] keyList,
final listSelectorInterface di) {
// set up the dialog
adb = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
adb.setCancelable(false);
adb.setItems(itemList, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
// when an item is clicked, notify our interface
public void onClick(DialogInterface d, int n) {
d.dismiss();
di.selectedItem(keyList[n], itemList[n]);
}
});
adb.setNegativeButton("Cancel", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
// when user clicks cancel, notify our interface
public void onClick(DialogInterface d, int n) {
d.dismiss();
di.selectorCanceled();
}
});
adb.setTitle(title);
// show the dialog
adb.show();
return this;
}
}
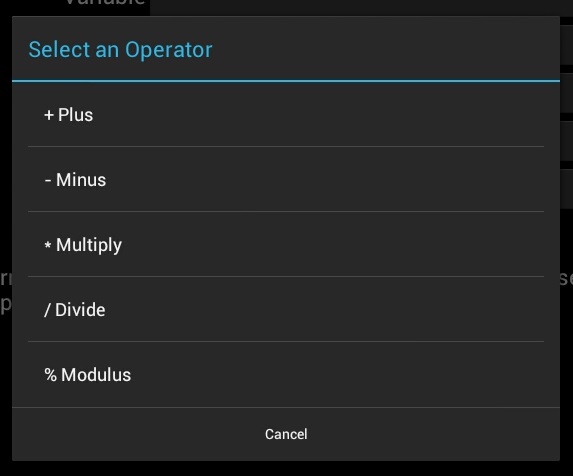
Example of how to call the ListSelectorDialog and handle selected item input:
ListSelectorDialog dlg = new ListSelectorDialog(this, "Select an Operator");
String[] listk = new String[] {"+", "-", "*", "/", "%"};
String[] listv = new String[] {"+ Plus", "- Minus", "* Multiply", "/ Divide", "% Modulus"};
dlg.show(listv, listk, new ListSelectorDialog.listSelectorInterface() {
public void selectorCanceled() {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"User Canceled the request!", 1).show();
}
public void selectedItem(String key, String item) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"User Has selected item '"+item+"' having key '"+key+"'!", 1).show();
}
});
Published by: Thomas Penwell
Initially published on: July 25, 2014
Article last modified on: Sunday, January 31, 2016.




